Towards Efficient Generative Large Language Model Serving: A Survey From Algorithms to Systems
面向高效生成式大语言模型的服务:从算法到系统的综述
随着 AI 的飞速发展,特别是伴随着 ChatGPT 的诞生,标志着深度学习已经进入了大语言模型(Large Language Models,LLM)的时代。然而,LLM 由于其本身的复杂性和大规模而给部署和服务带来了前所未有的挑战。
来自卡内基梅隆大学的 Catalyst 团队在他们的最新综述论文中,从机器学习系统的研究视角出发,详细分析了前沿 LLM 推理从算法到系统的产生的重大变革。
Abstract 摘要
In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), generative large language models (LLMs) stand at the forefront, revolutionizing how we interact with our data. However, the computational intensity and memory consumption of deploying these models present substantial challenges in terms of serving efficiency, particularly in scenarios demanding low latency and high throughput. This survey addresses the imperative need for efficient LLM serving methodologies from a machine learning system (MLSys) research perspective, standing at the crux of advanced AI innovations and practical system optimizations. We provide in-depth analysis, covering a spectrum of solutions, ranging from cutting-edge algorithmic modifications to groundbreaking changes in system designs. The survey aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state and future directions in efficient LLM serving, offering valuable insights for researchers and practitioners in overcoming the barriers of effective LLM deployment, thereby reshaping the future of AI.
在快速发展的人工智能 (AI) 领域,生成式大语言模型 (LLM) 处于最前沿,彻底改变了我们与数据交互的方式。然而,部署这些模型所需的计算强度和内存消耗对服务效率提出了巨大的挑战,特别是在需要低延迟和高吞吐量的场景中。这篇综述从机器学习系统(MLSys)研究的角度探讨了对高效 LLM 服务方法的迫切需求,这是先进 AI 创新和实用系统优化的关键所在。我们给出了深入的分析,涵盖了一系列解决方案,从尖端算法的改进到系统设计的突破性优化。该综述旨在全面了解高效 LLM 服务的现状和未来方向,为研究人员和从业者提供宝贵的见解,帮助他们克服有效部署 LLM 的障碍,从而重塑 AI 的未来。
Taxonomy 分类
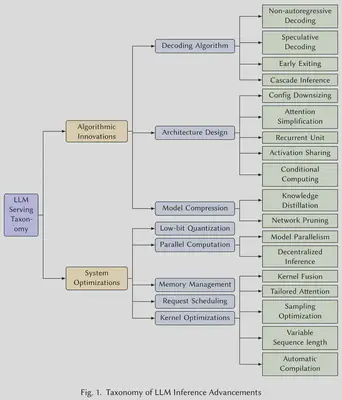
该综述从算法创新和系统优化两个维度展开介绍。顾名思义,前者是在偏上层的算法(模型)层面的工作,后者是在偏下层的系统层面的工作。
Algorithmic Innovations 算法创新
Decoding Algorithm 解码算法
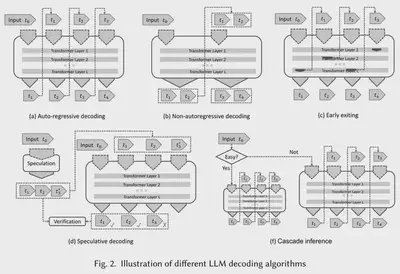
现有的 LLM 多采用自回归解码(Auto-Regressive Decoding)机制,这会导致极低的计算效率。所以很自然地可以想到放弃这个范式,采用更高效的解码算法。
| 关键技术 | 细节扼要 | 代表工作 |
|---|---|---|
| 非自回归解码 | 打破 token 之间的依赖关系,并行解码输出 但是精度不及自回归解码 |
/ |
| 投机式推理 | 添加条件分支,并行推理(预测),选择置信度更高的结果 预测过程需要足够轻量且准确 |
SpecInfer |
| 提前退出 | 在中间层满足置信度时提前退出推理 | DeeBERT |
| 级联推理 | 部署级联多个不同规模的 LLM,分别处理不同复杂度的推理请求 | CascadeBERT FrugalGPT |
Architecture Design 架构设计
这里的“架构”特指模型架构,具体到 LLM 上面来看,主要是 Attention 算子的设计。当然,作者团队也罗列出了一些其他的架构设计技术。
| 关键技术 | 细节扼要 | 代表工作 |
|---|---|---|
| 配置缩小 | 顾名思义,就是直接减少模型规模 例如,使用浅层编解码器、权重共享 但是会显著影响下游任务性能 |
/ |
| 注意力简化 | 热门研究方向,近期工作非常多 或降低长序列 Attention 的计算复杂度,或减少 K/V Cache |
Sliding window attention Hash-based attention Dilated attention 更多详见后文 |
| 激活共享 | 顾名思义 | Multi-query attention (MQA) Group-query attention (GQA) |
| 条件计算 | 指的就是混合专家模型(Mixture of Experts,MoE) 是一种稀疏的方法 |
TaskMoE FasterMoE |
| 循环单元 | 尝试将 RNN 重新引入 LLM | RetNet |
关于注意力简化的工作有很多,下图则列出了几种典型的注意力机制改进方法。

Model Compression 模型压缩
模型压缩是我们非常熟知的老朋友了。它包含三大关键技术:剪枝、量化和蒸馏。本小节则主要介绍了网络剪枝和知识蒸馏两大技术,量化在系统优化章节介绍。
| 关键技术 | 细节扼要 | 代表工作 |
|---|---|---|
| 知识蒸馏 | 用大模型指导小模型的训练 在特定的下游任务能展现出优良的性能 |
Alpaca Vicuna WizardLM |
| 网络剪枝 | 分为结构化剪枝和半结构化剪枝 需要重新训练,可能带来过高的部署成本 |
Flash-LLM |
System Optimizations 系统优化
Low-bit Quantization 低比特量化
- 量化感知训练(Quantization-Aware Training,QAT)
- 训练后量化(Post-Training Quantization,PTQ)
Parallel Computation 并行计算
本文分两个小节介绍并行计算,即模型并行和去中心化计算。这两大技术都是我们所熟知的。
首先,模型并行(Model Parallelism,MP)分为张量并行(Tensor Parallelism,TP)和流水线并行(Pipeline Parallelism,PP)。要注意,数据并行(Data Parallelism,DP)不属于模型并行的范畴。
| 关键技术 | 代表工作 |
|---|---|
| TP | PaLM, GShard, GSPMD Alpa, FlexFlow, Galvatron |
| PP | / |
其次,去中心化计算即分布式计算,它使消费级的 GPU 部署 LLM 成为可能。但是,其中有不少挑战,例如设备异构性、有限的计算和内存容量、低带宽网络、故障宽容和隐私保护等。
Memory Management 内存管理
内存管理是 LLM 部署和推理的关键挑战,这是因为 Transformer 的自回归解码是访存密集型任务。随着对长序列推理的需求不断增长,与模型权重和其他激活所需的工作空间相比,K/V Cache 的内存占用成为主要优化目标。
| 代表工作 | 细节扼要 |
|---|---|
| FasterTransformer | 预先分配一块具有最大序列长度假设的连续内存 ❗严重浪费内存 |
| vLLM (PagedAttention) | 将 K/V Cache 划分为不连续的内存块 |
| SpecInfer | Tree Attention:利用深度优先遍历,消除共享相同前缀的多个输出序列的冗余 K/V Cache |
| LightLLM | 更细粒度的 token 内存管理 |
Request Schedudling 请求调度
请求调度也是 LLM 部署和推理的一个重要的可优化方向。现有的工作已经集成了多种请求调度策略。
| 调度策略 | 细节扼要 | 应用 |
|---|---|---|
| FCFS | 先来先服务 | Orca |
| Continuous Batching | 数据可用则立即处理,而不是等固定大小的批次数据积累后再处理 | vLLM |
| Inflight Batching | 在当前计算任务进行时,存储其他输入数据 | TensorRT-LLM |
| Skip-join MLFQ | 对输入长度较短的请求进行优先级排序 | FastServe |
Kernel Optimization 内核优化
这部分的优化位于最底层,同样也是 LLM 部署和推理的一个重要的可优化方向。相关的技术包括内核融合、特定 Attention 算子、采样优化、变长序列、自动编译等。
其中,我们详细说明一下变长序列优化技术。它指的是将长度不一的若干序列组合成一个 batch 进行推理,这样一来短序列后面需要 padding 零填充,所以会导致显存浪费。目前有效的解决方案是打包技术,将序列映射到连续的内存空间中。
Software Frameworks 软件框架
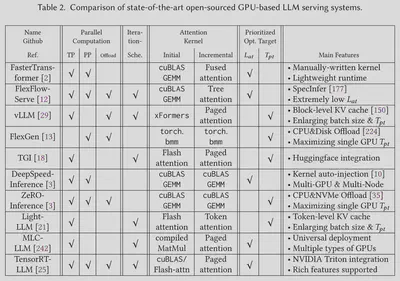
论文还对一些目前最先进的基于 GPU 的开源 LLM 推理系统进行了深入的分析,并从多个方面总结了它们在设计与实现上的差异。
Future Direction 未来方向
Development and Enhancement of Hardware Accelerators. Future progress in enhancing generative LLM serving efficiency could be significantly driven by the development and refinement of specialized hardware accelerators, complemented by a co-design approach that aligns hardware and software optimizations. For instance, integrating memory closer to processing units or optimizing chip architectures to better align with the data flow of LLM algorithms can lead to substantial reductions in latency and energy consumption.
专用硬件加速器的发展:生成型 LLM 服务效率的显著提升可能在很大程度上依赖于专用硬件加速器的发展和提升,尤其是软硬协同设计方法。例如,让内存单元更加接近处理单元,或是针对 LLM 算法数据流优化芯片架构,这些硬件优化可以在很大程度上为 LLM 推理在软件层面带来便利和机会。
Efficient and Effective Decoding Algorithms. The development of more efficient decoding algorithms could substantially improve serving efficiency. Motivated by the demand for more resource-efficient ways to utilize the vast knowledge encapsulated within LLMs, future work could explore alternative approaches to the traditional auto-regressive methods and unlock the generation speed for real-time applications while maintaining the decoding quality. One promising direction is generalized speculative inference as it enables preserving the same generation quality.
高效且有效的解码算法:受对实时应用更快生成速度的需求驱动,一个有前途的方向是广义的投机式推理,不仅会带来显著加速,同时保持相同的生成质量。
Long Context/Sequence Scenarios Optimization. As the application of LLMs continues to expand into more sophisticated scenarios, the demand for processing longer contexts or sequences is steadily growing. Serving LLMs with long-sequence workloads requires resolving the challenges from both the algorithm and system sides.
For the LLM serving systems, longer sequence brings critical challenges, including more memory consumption and access of KV cache and quadratic increasing computational complexity of self-attention.
长上下文/序列场景优化:随着应用场景变得更加复杂,处理更长的上下文或序列的需求不断增长。服务长序列负载的 LLM 需要解决算法和系统两方面的挑战,包括更多的显存开销和 K/V Cache 访存开销,以及 Attention 的二次计算复杂度。
Investigating Alternative Architectures. Although Transformer models and self-attention mechanisms currently dominate the landscape of LLMs, exploring alternative architectures is a promising direction for future research. The field of DL has historically seen a constant alternation of dominant architectures, with each new paradigm shift bringing about significant advancements. Given this trend, it’s important to consider other architectural approaches that could offer distinct advantages, especially for improved computational efficiency.
探索替代基础架构:尽管 Transformer 模型和自注意力机制目前在 LLM 领域占据主导地位,但探索替代架构是未来研究的一个有前景的方向。深度学习领域历来见证了主导架构的不断更替,每一次新的范式转变都会带来重大进步。鉴于这种趋势,考虑其他可以提供明显优势的架构方法非常重要,特别是在提高计算效率方面。
Exploration of Deployment in Complex Environments. As the application of LLMs expands, a crucial future direction involves exploring and optimizing their deployment across various complex environments. This exploration goes beyond traditional cloud-based deployments to include scenarios like edge computing, hybrid computing (combining cloud and edge computing), decentralized computing, and the utilization of more affordable resources like spot instances. Each of these environments presents unique challenges and opportunities for LLM serving.
探索复杂环境的部署:随着 LLM 应用的扩展,探索并优化它们在各种复杂环境中的部署成为一个关键的未来方向。这一探索不仅限于传统的基于云的部署,还包括边缘计算、混合计算(云边协同)、去中心化计算以及廉价的可抢占资源等。这些环境中的每一个都为 LLM 服务带来了独特的挑战和机遇。
Automatic Adaptation to Specific Requirements. The diverse application-specific requirements create a wide range of innovative LLM serving optimization opportunities, such as parameterefficient fine-tuning, retrieval from external vector storage, online learning and knowledge updates, multi-modal workloads, and chaining together different LLMs’ capabilities. These unique challenges also demand automatic and smooth integration of LLM serving techniques into existing IT infrastructures by extending the optimization space to the whole LLM lifetime.
特定需求的自适应:应用特定需求的多样性创造了一系列创新的 LLM 服务优化机会,例如模型微调、向量数据库检索、多模态负载等等。这些独特的挑战也要求将 LLM 服务技术自动且顺利地集成到现有 IT 基础设施中,将优化空间扩展到整个 LLM 生命周期。